By Madeleine Rowley for The Free Press
While the border crisis has become a major liability for President Biden, threatening his reelection chances, it’s become a huge boon to a group of nonprofits getting rich off government contracts.
Although the federally funded Unaccompanied Children Program is responsible for resettling unaccompanied migrant minors who enter the U.S., it delegates much of the task to nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) that run shelters in the border states of Texas, Arizona, and California.
And with the recent massive influx of unaccompanied children—a record 130,000 in 2022, the last year for which there are official stats—the coffers of these NGOs are swelling, along with the salaries of their CEOs.
“The amount of taxpayer money they are getting is obscene,” Charles Marino, former adviser to Janet Napolitano, the secretary of the Department of Homeland Security under Obama, said of the NGOs. “We’re going to find that the waste, fraud, and abuse of taxpayer money will rival what we saw with the Covid federal money.”
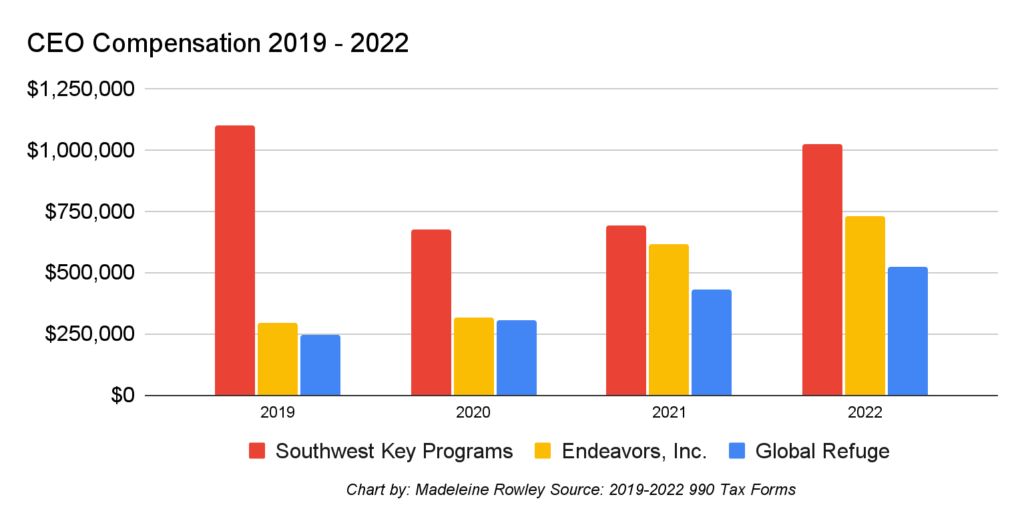
The Free Press examined three of the most prominent NGOs that have benefited: Global Refuge, Southwest Key Programs, and Endeavors, Inc. These organizations have seen their combined revenue grow from $597 million in 2019 to an astonishing $2 billion by 2022, the last year for which federal disclosure documents are available. And the CEOs of all three nonprofits reap more than $500,000 each in annual compensation, with one of them—the chief executive of Southwest Key—making more than $1 million.
Some of the services NGOs provide are eyebrow-raising. For example, Endeavors uses taxpayer funds to offer migrant children “pet therapy,” “horticulture therapy,” and music therapy. In 2021 alone, Endeavors paid Christy Merrell, a music therapist, $533,000. An internal Endeavors PowerPoint obtained by America First Legal, an outfit founded by former Trump aide Stephen Miller, showed that the nonprofit conducted 1,656 “people-plant interactions” and 287 pet therapy sessions between April 2021 and March 2023.
Endeavors’ 2022 federal disclosure form also shows that it paid $5 million to a company to provide fill-in doctors and nurses, $4.6 million for “consulting services,” $1.4 million to attend conferences, and $700,000 on lobbyists. In 2021, the NGO shelled out $8 million to hotel management company Esperanto Developments to house migrants in their hotels. Endeavors, which gets 99.6 percent of its revenue from the government according to federal disclosure forms, declined to comment to The Free Press.
The Administration for Children and Families, a division of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, funds the nonprofits through its Office of Refugee Resettlement, and its budget has swelled over the years—from $1.8 billion in 2018 to $6.3 billion in 2023. The ORR is expected to spend at least $7.3 billion this year—almost all of which will be funneled to NGOs and other contractors.
When asked about the funding increase during a January media event, Krish O’Mara Vignarajah, the chief executive of Global Refuge said, “We’ve grown because the need has grown.” The nonprofit did not make Vignarajah available for an interview.
But while it’s true the number of migrants has exploded in recent years, critics say these enormous federal grants far exceed the current need. The facilities themselves are generally owned by private companies and are leased to the NGOs, which house the unaccompanied minors and attempt to unite them with family members or, if that’s not possible, people who will take care of them—their so-called sponsors. The ORR does not publicly list the specific number of shelters it funds in its efforts to house migrants, a business The New York Times once described as “lucrative” and “secretive.”
While some NGOs have long had operations at the border, “what is new under Biden is the amount of taxpayer money being awarded, the lack of accountability for performance, and the lack of interest in solving the problem,” said Jessica Vaughan, director of policy studies at the Center for Immigration Studies, a think tank that researches the effect of government immigration policies and describes its bias as “low-immigration, pro-immigrant.”
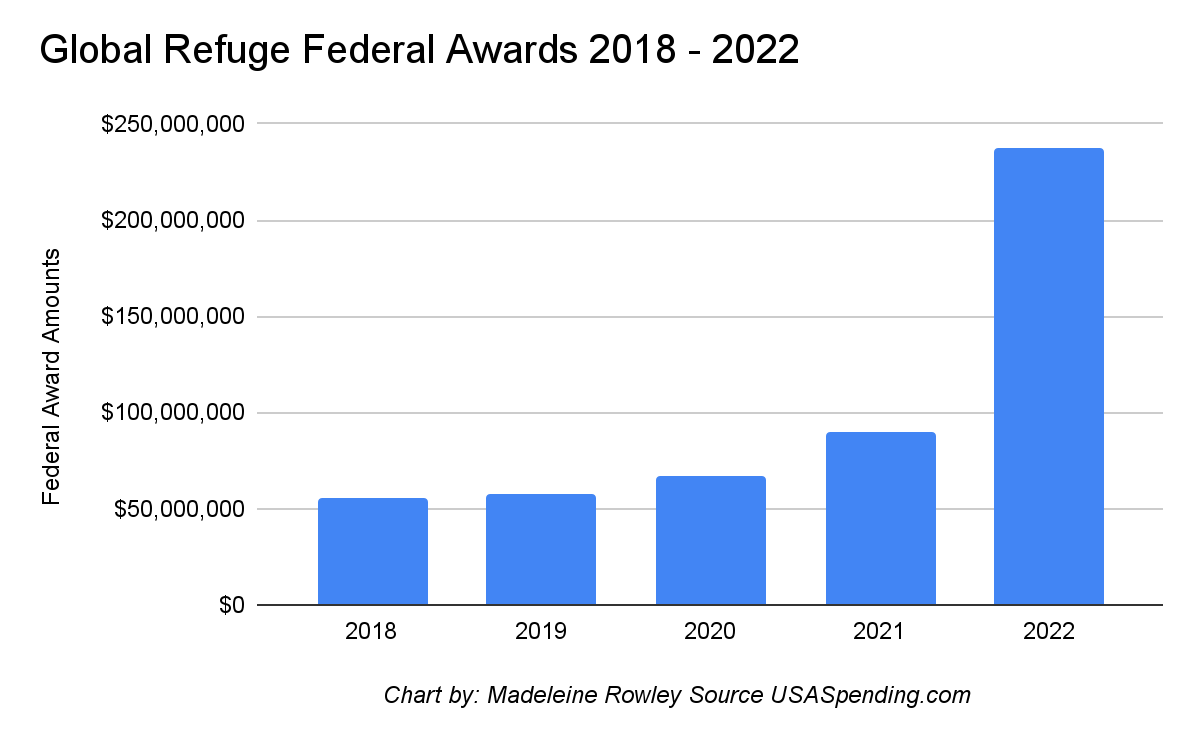
Consider Global Refuge, based in Baltimore, Maryland. In 2018, according to its federal disclosure form, the Baltimore-based nonprofit had $50 million in revenue. By 2022, its revenue totaled $207 million—$180 million of which came from the government. That year, $82 million was spent on housing unaccompanied children. Global Refuge also granted $45 million to an organization that facilitates adoptions as well as resettling migrant children.
Now Global Refuge employs over 550 people nationwide, and CEO Vignarajah said in January that the nonprofit plans to expand to at least 700 staffers by the end of 2024.
Vignarajah, a former policy director for Michelle Obama when she was first lady, took the top job at Global Refuge in February 2019 after she lost her bid to be elected governor of Maryland. She has since become one of the most prominent advocates for migrants crossing the southern border, appearing frequently on MSNBC and other media as an immigration advocate. Her incoming salary was $244,000, but just three years later, her compensation more than doubled to $520,000.
In 2019, Global Refuge housed 2,591 unaccompanied children while spending $30 million. Three years later, the NGO reported that it housed 1,443 unaccompanied children at a cost of $82.5 million—almost half the number of migrants for more than double the money.
In a statement to The Free Press, Global Refuge spokesperson Timothy Young said that while in care, “Unaccompanied children attend six hours of daily education and participate in recreational activities, both at the education site and within the community.”
The man with the $1 million salary is Dr. Anselmo Villarreal, who became CEO of Southwest Key Programs, headquartered in Austin, Texas, in 2021. (Villarreal took a drop in pay compared to his predecessor, Southwest Key founder Juan Sanchez, who paid himself an eye-popping $3.5 million in 2018.)
Despite a number of scandals in the recent past, including misuse of federal funds and several instances of employees sexually abusing some of the children in its care, Southwest Key continues to operate—and rake in big government checks. In 2020, the year of Covid-19, its government grant was $391 million; by 2022, its contract was nearly $790 million.
To read the rest of this article, please visit the The Free Press.
The preceding article originally appeared on May 14, 2024 at The Free Press and is made available here for educational purposes only. This constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in Title 17 U.S.C. section 106A-117 of the U.S. Copyright Law. Photo above: A group of migrants try to cross a barbed wire fence to reach the U.S., as seen from Ciudad Juarez, Mexico, on March 20, 2024. (Photo by Herika Martinez via Agence France-Presse)



